Canada
Quick reference
General issues: British colony/Self government 1851-1868
Country name on general issues: Canada
Currency: 1 Shilling = 12 Pence 1851-1859, 1 Dollar = 100 Cents 1859-1868
Population: 2 506 000 in 1861
Political history Canada
Exploration and French rule
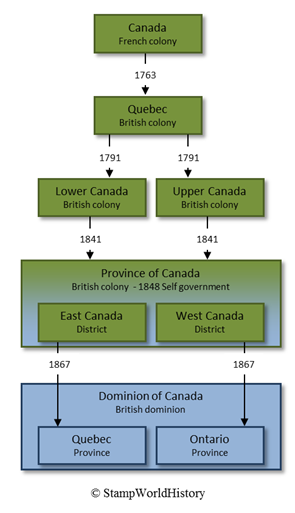
Political developments 1763-1867
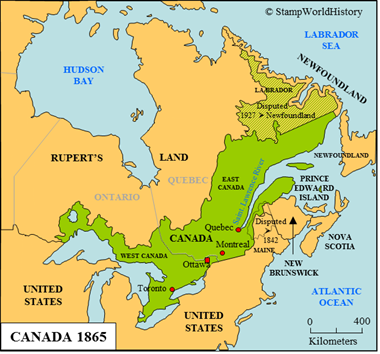
The colony of Canada – not to be confused with the later Dominion of Canada – was located in North America and comprised part of the provinces of Ontario and Quebec of modern day Canada. Prior to colonization, Canada was inhabited by Amerindian and Inuit peoples. Some of these peoples were nomadic hunter gatherers and some were sedentary, depending on agriculture. The most important Amerindian peoples were the Algonquian, Huron and Iroquois. The first European to explore Canada was the French explorer Jacques Cartier in 1534. The French first settled Canada in 1608 when Quebec was founded. The French, subsequently, established the colony of Canada as part of New France, the collective name for the French possessions in North America.
British rule
French rule would last until 1763, when the French possessions, in what today constitutes Canada, were ceded to the British. The British renamed the colony Quebec. To accommodate the French population, Quebec was allowed to retain French legislation, culture and language by way of the Quebec Act of 1774. The United States War of Independence brought about major changes for the colony. Significant numbers of Loyalists settled in Quebec.[1]Loyalists were thus called because they remained loyal to the British during the War of Independence. The Loyalists brought with them English legislation, culture and language. For this reason, Quebec was split into the colonies of Upper and Lower Canada in 1791 – Upper Canada for the British and Lower Canada for the French. In following decades, the number of people of British descent further increased through immigration from the British Isles and, eventually, the British became the majority of the population. The British now changed their policy and, with the aim to assimilate the French minority, Upper and Lower Canada were united to form the Province of Canada in 1841. The colonies of Upper and Lower Canada became the districts of West and East Canada. The Province of Canada gained self government in 1848 and joined the federal Dominion of Canada in 1867 – together with Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. At the same time, the Province of Canada was split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec as we know them today.
Establishing the borders
The borders of the Province of Canada were established in a few steps. When the French ceded Canada to the British in 1763, the colony stretched from the coast of Labrador in the north to beyond the Great Lakes in the south. The territory south of the Great Lakes was ceded to the United States after the American War of Independence in 1783. In 1809, the ‘coast of Labrador’ was awarded to Newfoundland. Just exactly how far the ‘coast of Labrador’ extended inland would be disputed until 1927, when the borders were defined by the British Judicial Committee of the Privy Counsel – the court of final appeal for British possessions. Part of the ruling of the Counsel is disputed by current Quebec until today. The last military conflict over Canada was fought during the War of 1812 with the United States – a war that ended in the status quo ante bellum. Finally, the border with the United States was settled in 1842 when agreement was reached on the disputed border with the United States state of Maine. As part of the Dominion of Canada, the provinces of Ontario and Quebec would see their territory enlarged substantially to the north and the west at the expense of Rupert’s Land, later called Northwest Territories. The present day borders of Ontario and Quebec were established in 1912.
Economy
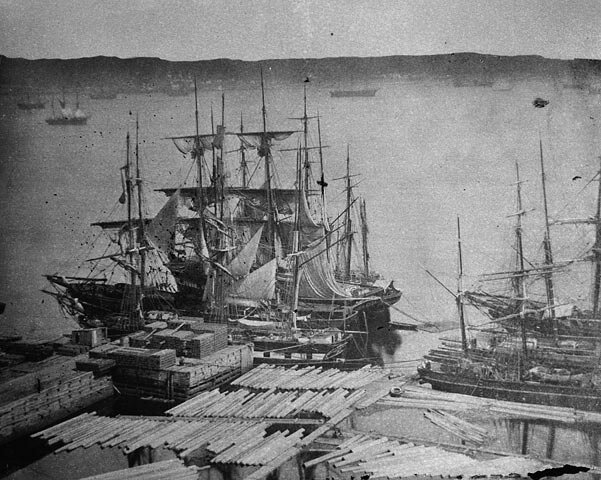

In the 19th century timber was the main product of Canada. Here ships are loaded with timber in Quebec around 1860.
Economically, from the first days of colonization, the fur trade was of key importance. The French developed a network of trade routes and built forts to protect the trade routes and serve as trading posts. When the fur trade declined, and British settlers came to Canada, forestry and agriculture developed. In the 20th century, manufacturing and services industries were developed – services now being the most important sector. Of the Canadian provinces and territories, modern day Ontario ranks first and Quebec third in terms of GDP.
Demography
During French rule, the number of French settlers was small when compared to, for example, the number of British settlers in the British colonies to the south, now part of the United States. French settlement was concentrated in what today constitutes Quebec. British settlers first arrived in significant numbers after the United States War of Independence in 1783. The 19th century saw large numbers of immigrants coming to Canada – the population doubled between 1840 and 1850. Immigration continued well into the 20th century. Today Ontario is by far the most populous province of Canada – Quebec ranks second. While the largest population group in Ontario is of British descent, in Quebec the largest group is of French descent. French is the official language of Quebec. The indigenous peoples account for about 3% of the population of both Ontario and Quebec.
Postal history Canada
The Province of Canada issued its first stamps in 1851. The first set shows portraits of Queen Victoria, Prince Albert – the Prince Consort – and the French explorer Jacques Cartier. Two of the portraits of Queen Victoria are of the ‘Chalon Heads’ type.[2]For more about the Chalon Heads, please refer to the profile of Nova Scotia. The fur trade is honored with the image of a beaver on one of the stamps of the set. A second set was issued in 1859, after the introduction of the dollar as the new currency. The designs of the second set are the same as those of the first set. Almost all stamps of the Province of Canada rank in the high to very high catalog value ranges. The stamps of the Province of Canada were superseded by the issues of the Dominion of Canada in 1868.
Album pages
← Previous page: Canadian Provinces - British Columbia & Vancouver IslandNext page: Canadian Provinces - New Brunswick →