פלשתינה فلسطين

Palestine
British mandated territory

Palestine
Palestinian Authority
Quick reference
General issues: British military administration, Egyptian Expeditionary Force 1918-1920, British civil administration 1920-1922, British mandated territory 1922-1948, Palestinian Authority 1994-Present
Country name on general issues: E.E.F., Palestine, Palestinian Authority
Related issues:
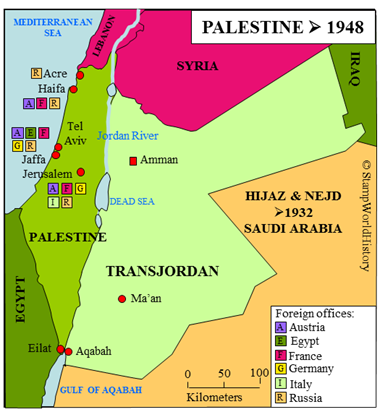
- Foreign offices Italy, Jerusalem 1909-1911
- Foreign offices Russia, Jaffa 1909-1910, Jerusalem 1909-1910
- Jaffa local issue 1909, Gaza local issue 1917
- Indian Expeditionary Force 1914-1922
- Egyptian occupation of Palestine 1948-1967
- Jordanian occupation of Palestine 1948-1950
- Indian Forces in Egypt 1965
Currency: 1 Piaster = 10 Millièmes, 1 Egyptian pound = 1000 Millièmes 1918-1927, 1 Palestinian pound = 1000 Mils 1927-1948, 1 New Shekel = 100 Agorot, 1 Jordanian Dinar = 1000 Fils (= 1000 Mils), 5 New Shekel = 1000 Fils (= 1000 Mils) 1994-Present
Population: Palestine 737 000 in 1920, 1 912 000 in 1946, Gaza 1 022 000 in 1997, West Bank 1 873 000 in 1997
Political history Palestine
From Ottoman rule to British mandated territory
Palestine is located in the Middle East in western Asia. In the 19th century Palestine is part of the Ottoman Empire. In 1917, during WWI, the territory is occupied by the British – the Egyptian Expeditionary Force – who at first establish a military administration. In 1920, civil administration is established and in 1922 the League of Nations formally approves of what is then called Palestine to be administered by Great Britain as a mandated territory. The borders have, at that point, for a large part been determined through the treaty of Sèvres signed in 1920 by which the British and the French agreed upon their respective spheres of influence in the former parts of the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East.
Growing Jewish influence
Palestine has long had a mainly Arab population. From the end of the 19th century a growing number of Jews will emigrate to Palestine. At the same time, Zionism gains influence. Zionism is a movement aiming at the establishment of a Jewish state. A major step in achieving this aim is taken, in 1917, with the Balfour declaration, in which Great Britain recognizes the right of the Jewish people to a ‘national home’. The establishment of a ‘national home for the Jewish people’ next becomes an important element in the British mandate over Palestine.
British mandated territory
During the British mandate, tension rises between the Arab and ever growing Jewish population groups in Palestine. After WWII, the United Nations, in 1947, present a plan for the establishment of both an Arab and a Jewish state in Palestine with Jerusalem under international control. The plan is rejected by the Arab population and civil war breaks out.
The state of Israel
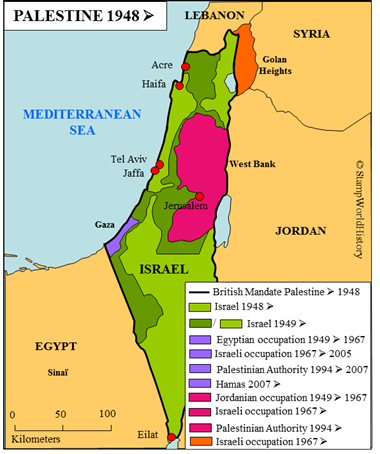
When the British mandate ends in 1948, the Jewish state is proclaimed as the republic of Israel. The same day, a number of Arab countries in the region declare war on Israel. The war ends, in 1949, with a cease fire agreement. Part of the cease fire agreement is the establishment of provisional borders. Compared to the United Nations plan from 1947, Israel gains territory. The remaining territory is put under control of Egypt[1]Gaza and Jordan[2]The West Bank . Many of the Arabs in the country – subsequently called Palestinians – seek refuge in Gaza, the West Bank and neighboring Jordan and Lebanon.
War
In subsequent years Israel and the Arab countries will engage in war several times. In 1956, Israel supports Great Britain and France in the Suez crisis and occupies Gaza and the Sinai. Under United Nations pressure Israel withdraws in 1957, after which the United Nations Emergency Force is deployed in the area. UNEF will be active in the region until 1967. In 1967, the Six Day War breaks out. Israel is militarily superior to the Arab countries. The war ends in Israeli occupation of Gaza and the Sinai, the West Bank and the Golan Heights, that are part of Syria. In 1973, war again breaks out. This Yom Kippur War ends in a status quo ante bellum. As of 1978, Israeli forces are deployed several times in Lebanon, that at the time serves as a base for Palestinian militias fighting Israel.
The road to peace
At the end of the 1970’s, diplomatic initiatives aimed at peace are successful. In 1979, a peace agreement is signed with Egypt. A peace agreement with Jordan follows in 1994. Among other things the borders are agreed upon. Egypt and Jordan relinquish claims they may have had on Gaza and the West Bank, these territories to become part of the negotiations on the formation of a Palestinian state.
The Palestinian Authority
The Palestinians have organized themselves, in the 1960’s, as the Palestinian Liberation Organization – PLO – that initially focuses on an armed fight against Israel. In the 1970’s, the PLO approach becomes more political. After the peace agreement in 1994, the Palestinian Authority is formed that gains a certain amount of self government in Gaza and on the West Bank. In 2005, Israel fully withdraws from Gaza – although it still controls its borders and airspace. Israel has repeatedly invaded Gaza as reprisal for air attacks from Gaza. After internal conflicts, Hamas takes over power in Gaza in 2007, at the expense of the Palestinian Authority. Internationally, there is much support for a fully independent Palestinian state. A solution that accommodates both the Israeli and the Palestinians has yet to be found.
Postal history Palestine
Ottoman rule
In Ottoman times the stamps of Turkey were used in Palestine. A local issue appeared in Jaffa in 1909, an overprint commemorating the start of the reign of sultan Mehmet Resad. A further local issue appeared in Gaza in 1917. Due to a lack of Turkish 5 para stamps, Turkish 10 para stamps were locally overprinted with the new value. Several countries – Austria, Egypt, France, Germany, Italy and Russia – had offices abroad in Acre, Haifa, Jaffa and Jerusalem. The general issues of these countries, or the issues for the Levant, are used in these offices. Italy issues stamps specifically for use in its Jerusalem office, overprints reading ‘Gerusalemme’ and a new face value. Russia, likewise, issues stamps for the Jaffa and Jerusalem offices in 1909, these being previous issues for the Levant with an overprint reading ‘Jaffa’ or ‘Jerusalem’ and a new face value. The foreign offices were closed in 1914.
British rule
From 1918, stamps issued by the British military administration are used, stamps inscribed ‘E.E.F.’[3]‘Egyptian Expeditionary Force’ . These stamps are also used in other territories held by the British: Cilicia, Egypt, Lebanon, Syria, and (Trans-)Jordan. The British and British Indian forces also used field post stamps in the occupied territories, the forces from India using the ‘I.E.F.'(‘Indian Expeditionary Force’) overprints.
The E.E.F. issues are, from 1920, superseded by issues from the British civil administration and the British mandate administration. At first overprints are issued on the E.E.F. issues reading ‘Palestine’ in Arab, English and Hebrew. From 1927, definitives are issued also inscribed Palestine in Arab, English and Hebrew.
Israel and the occupied territories
In 1948, the stamps of the British administration were, in those parts of Palestine that became part of Israel, superseded by the issues of Israel. When, after the 1948-1949 war, the provisional borders were established, Gaza came under Egyptian control and the West Bank under Jordanian control. Egypt issued stamps for use in Gaza from 1948 until 1967. The forces from India, deployed in the Gaza and the Sinai after the Suez crises in 1956 as part of the United Nations Emergency Force, issued field post stamps in 1965. Jordan has issued stamps for the West Bank in 1948 and 1949. The West Bank was annexed by Jordan in 1950 and, from 1950 until 1967, Jordanian stamps have been used. After the Israeli occupation, Israeli stamps came into use in both Gaza and on the West Bank.
The Palestinian Authority
As of 1994, Israeli stamps are used concurrently with issues of the Palestinian Authority. In the Palestinian territories both the Israeli and Jordanian currencies are used, the Palestinians not having a currency of their own. The stamps are issued in Jordanian currency. In Gaza Hamas has issued stamps since 2009. These are recognized by the Palestinian Authority since 2014 for use on domestic mail.[4]The Hamas issues are currently not listed by the worldwide catalogs.
Album pages
← Previous page: PakistanNext page: Philippines →