British East Africa
British protectorate

Uganda
British protectorate
Quick reference
General issues: British East Africa & Uganda protectorates postal union 1903-1920
Country name on general issues: East Africa and Uganda Protectorates
Special issues: Indian Expeditionary Force 1914-1922, Occupation of German East Africa 1917-1920
Currency: 1 Rupee = 16 Anna 1901-1907, 1 Rupee = 100 Cent 1907-1920
Population: 2 549 000 in 1903
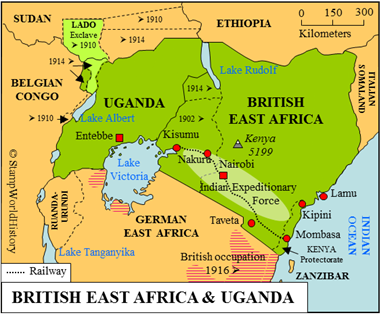
Political history British East Africa & Uganda
British East Africa and Uganda are two British protectorates in eastern Africa. Since 1888, the British have been active in eastern Africa through the British East Africa Company, established in 1887. The rights of the British East Africa Company are transferred to the British government in 1893 for Uganda and in 1895 for British East Africa. The British government subsequently forms the protectorates of Uganda and British East Africa in 1894 and 1895 respectively.
The borders of the protectorates are adjusted several times after their formation. In 1902, a large part of Uganda is transferred to British East Africa to bring the construction of the railway from Mombasa to Lake Victoria under one administration. A further border adjustment between British Africa and Uganda is effected in 1914, the borders between these countries thus being established as we know them until today. More border adjustments are effected with Belgian Congo in 1910 and 1914 and with Sudan in 1910 and 1914. The Lado exclave – leased from 1894 until 1910 by Leopold II and administered from Congo Free State, later Belgian Congo – is returned to the British in 1910, upon which it is transferred to Sudan, a small part in 1914 to be transferred back to Uganda.

Mount Kenya National Park
In WWI, British East Africa and Uganda are a staging ground for the attack on German East Africa. In the south of British East Africa units of the Indian Expeditionary Force from British India have their quarters. The British – supported by the Belgians from Belgian Congo – attack the mainland of German East Africa in 1916 to gradually occupy large parts of it. The German military command capitulates in 1918. After WWI, German East Africa is divided between Belgium and Great Britain as the mandated territories of Ruanda-Urundi and Tanganyika.
Uganda is a British protectorate until 1962 when first it gains self government and next it becomes independent within the British Commonwealth. British East Africa in 1920 becomes the colony of Kenya that in 1963 will become independent within the British Commonwealth.
British East Africa and Uganda cooperate in several ways, one of them being the postal union that is formed in 1901. The cooperation will, from 1922 until 1977, be continued within the East African Community which, from 1930, will also include Tanganyika and, from 1964, Zanzibar.
Postal history British East Africa & Uganda
In 1890, the first British post offices in British East Africa are opened in Lamu and Mombasa. The British East Africa Company issues stamps from 1890 until 1894. The issues from the British East Africa Company are, from 1895, superseded by the individual issues of British East Africa and Uganda, these to be superseded by the issues of the postal union between British East Africa and Uganda from 1903. The first issue of the postal union is a set of definitives.
During WWI, the Indian Expeditionary Force in its field post offices uses the stamps issued especially for the IEF. These are stamps of British India overprinted ‘I.E.F’ issued in 1914 and used until 1922. During the British occupation of German East Africa, in those parts that were under control of the British, stamps from British East Africa & Uganda were used, overprinted ‘G.E.A.’ for ‘German East Africa’ from 1917.
The stamps of the postal union of British East Africa & Uganda were, from 1922, superseded by the issues of the East African Community. These again are superseded by the issues of independent Kenya and Uganda.
Album pages
← Previous page: British East AfricaNext page: British Indian Ocean Territory →