Guinea
Quick reference
General issues: Republic 1958-Present
Country name on general issues: Guinée
Currency: 1 Franc = 100 Centimes 1958-1960, 1 (Guinea) Franc = 100 Centimes 1960-1972, 1 Syli = 100 Kauris 1972-1986, 1 (Guinea) Franc =100 Centimes 1986-Present
Population: 3 069 000 in 1958, 11 750 000 in 2013
Political history Guinea
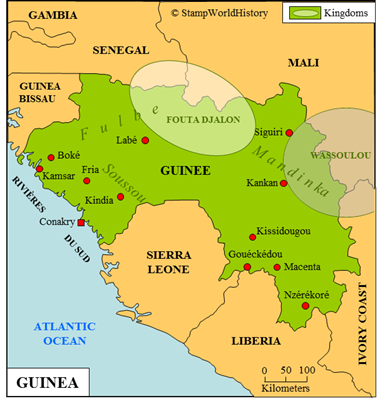
Guinea is located in western Africa. In the middle of the 19th century the future Guinea is home to a number of Niger-Congo peoples – the most important being the Fulbe, the Mandinka and the Soussou. Relations with European traders have existed in Guinea since the 16th century. In the mid 19th century the French sign treaties with local rulers in the coastal region thus forming protectorates. These protectorates are grouped together in 1882 as the protectorate of the Rivières du Sud, administered from Senegal. In 1891, the Rivières du Sud protectorate is annexed by France as the colony of French Guinea. French Guinea, in 1895, becomes part of French West Africa, the federation of French possessions in western Africa established in 1895.
Starting from the coastal region, the French, in subsequent years, extend their control to the hinterland. In the process, the French meet opposition, most notably from two kingdoms – Fouta Djallon and Wassoulou. Fouta Djallon is conquered by the French in 1896 and Wassoulou in 1898. Although most of French Guinea is thus brought under French rule, pockets of resistance will exist until the early 20th century.
The borders of French Guinea with British Sierra Leone, Portuguese Guinea and independent Liberia are established in 1882, 1886 and 1892 respectively. The borders of French Guinea within French West Africa are, by and large, established in 1899 when French Sudan is split up and several provinces of French Sudan become part of French Guinea.
French Guinea, as a result of the reorganization of the French colonial empire in 1946, becomes a French overseas territory. In 1958, French Guinea gains independence as the republic of Guinea.
Guinea has known a political history dominated by authoritarian leaders – the first democratic elections to be held in 2010. Guinea is rich in natural resources, owning half of the worlds reserves of bauxite. The political context however has prevented Guinea from taking full advantage of this riches.
Postal history Guinea
The first stamps used in what is to become Guinea are, from 1881, the general issues for the French colonies. From 1887 until 1892, the stamps of Senegal are used. Once French Guinea is established as a separate colony, stamps are issued from 1892. The stamps of French Guinea are, from 1944, superseded by those of French West Africa and from 1959 by those of independent Guinea.
Album pages
← Previous page: Griqualand WestNext page: Guinea-Bissau →