سورية

Syria
Arab Kingdom
Syria
Mandated territory

Syria
Republic

Syria
Arab republic
Quick reference
General issues: Kingdom 1920, Allied military administration/T.E.O. 1919-1920, French military administration/O.M.F. 1920-1923, French mandated territory of Syria & Greater Lebanon 1923-1924, French mandated territory of Syria/State of Syria 1924-1930, French mandated territory of Syria/Republic of Syria 1930-1941, Republic 1941-1958, United Arab Republic 1958-1961, Arab republic 1961-Present
Country name on general issues: Arabian government in Arabic, Syrian Arabian government in Arabic, T.E.O., O.M.F., Syrie, Republique Syrienne, Syria, U.A.R., Republique Arabe Unie, Syrian Arab Republic, Syrian A.R.
Special issues: Local issue Damascus 1920, Local issue Aleppo 1920, Local issue Ain-Tab 1921, Local issue Kilis 1921, Free French Forces 1942-1943
Currency: 1 Piaster = 10 Millièmes = 40 Para 1919-1920, 1 Pound = 100 Piaster = 1000 Millièmes 1920-Present
Population: 1 824 000 in 1924, 22 850 000 in 2013
Political history Syria
From Ottoman to French rule
Syria is located in the Middle East in western Asia. In the 19th century, Syria is part of the Ottoman Empire. When the Ottoman Empire sides with the Central Powers in WWI, British and Arab forces occupy Syria in 1918.
The Arabs fight for the establishment of an Arab state that will include Syria and other parts of the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East. In 1918, the Arabs in Damascus form the Arab government, and in 1920 the kingdom of Syria is proclaimed. However, the British and the French have, during WWI, decided on their respective spheres of influence in the Middle East. A division that, after WWI, is formalized in the treaty of Sèvres in 1920. In 1922, the League of Nations mandates the French for the administration of Syria and Greater Lebanon, a mandate that is ratified – now also by Turkey – in 1923 through the treaty of Lausanne.
Based on these agreements, Syria is put under the control of the OETA – the Occupied Enemy Territory Administration, which in French is called the ‘Administration Territoires Ennemis Occupés’. The OETA is established, in 1917, as a joint effort by the British and the French for the administration of the occupied territories in the Ottoman Empire.
The British, that have occupied Syria, withdraw in 1919 to be succeeded by the French. The French conquer Damascus in 1920 and put an end to the kingdom of Syria. Between 1920 and 1923, the French gain control over the rest of the mandated territory of Syria and Greater Lebanon. In Turkey the French go beyond the mandated territory to occupy Cilicia until 1922. The OETA is dissolved in 1920, Syria and Greater Lebanon being under direct French military administration from 1920 to 1923.
Shaping Syria
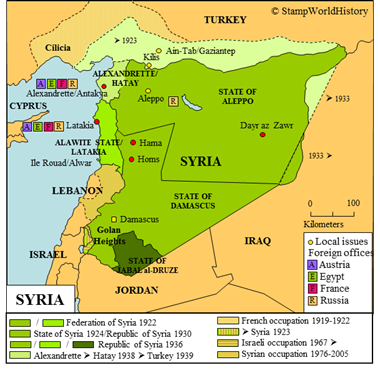
The French form a number political entities for the administration of the mandated territory in 1920 and 1921. This division is officially based on ethnic and religious grounds, although it is also suggested that the aim of the French was to prevent the establishment of a more powerful pan-Arab nation.
Four entities are formed that eventually will consolidate to form current Syria:
- the State of Aleppo, formed in 1920 with a Sunni Muslim majority;
- the State of Damascus, formed in 1920, also with a Sunni Muslim majority;
- the Alawite Territory, formed in 1920 with an Alawite majority, the Alawites being a Shia Muslim group;
- the State of Jabal al-Druze, formed in 1921 with a Druze majority, the Druze being a group with non Arab, non Muslim ethnic and religious origins.
The State of Aleppo, the State of Damascus and the Alawite Territory, in 1922, join to form the federation of Syria. When the federation of Syria is to become the State of Syria in 1924, the Alawite territory separates to become the Alawite State, that, in 1930, changes its name to Latakia. As a step on the road to independence – guiding the mandated territories to independence being part of the mandate – the State of Syria, in 1930, becomes the republic of Syria. The Alawite State and the State of Jabal al-Druze are added to the republic of Syria in 1936, establishing Syria as we still know it today.
Two entities are formed that show a largely separate development:
- the Sandjak of Alexandrette, formed in 1921 with a Turkish majority;
- the State of Greater Lebanon, formed in 1920 with a christian majority in Lebanon proper but also with large Shia and Sunni Muslim and Druze minorities in the territories added to form Greater Lebanon.
The Sandjak of Alexandrette is, from 1923 to 1925, made part of the state of Aleppo, but, subsequently, again becomes a separate administrative entity, that, in 1938, is transformed to the State of Hatay which becomes part of Turkey in 1939.
The state of Greater Lebanon, from 1926, is a separate mandated territory with its own political history, please refer to the country profile of Lebanon.
Aside from the formation of several political entities, a number of border corrections is effected during the French mandate:
- in 1922, the Ile de Rouad[1]The current Arwad. – that has been occupied by the French from 1916, is added to the Alawite Territory;
- in 1923, the borders with Turkey are redrawn, part of the French mandated territory as defined in the treaty of Sevres reverting to Turkey;
- also, in 1923, the Golan Heights are transferred from Palestine to the State of Damascus;
- finally, in 1933, a border correction with Iraq is effected.
WWII and independence
During WWII, the French administration is loyal to the Vichy regime – collaborating with Germany – in France. British and Free French Forces occupy the country in 1941. Syria proclaims independence in the same year. The French, however, claim a veto right on major decisions. Full independence is recognized by the French in 1944, the last French forces leave Syria in 1946.
After independence, Syria is confronted with a series of military coups from 1949 to 1958. In 1958, the strive for a pan-Arab nation leads to the formation of the United Arab Republic with Egypt. The Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser becomes head of state. The United Arab Republic is short lived: already, in 1961, Syria withdraws from the United Arab Republic to become the Arab republic of Syria. In 1963, the Ba’ath party comes to power. The Ba’ath party is, from 1971, led by Hafiz al-Assad who is succeeded by his son Bashar al-Assad in 2000.
Syria is one of the major contestants in the conflict with Israel, taking part in the 1948, 1967 and 1973 wars. Israel, in 1967, occupies the Golan Heights, which are under Israeli control to this day. In 1976, Syria becomes involved in the civil war in neighboring Lebanon. With a mandate from the Arab League, Syria invades Lebanon to end the conflict. Syria occupies parts of Lebanon and, as the conflict continues, will be in Lebanon until withdrawal in 2005.
When, from 2011, the Arab Spring leads to revolutions across many Arab states, in Syria several movements take up arms against the Assad regime. Since then, Syria is involved in civil war, Islamic State – IS or ISIL – being the most important and extreme movement involved.
Postal history Syria
Ottoman rule, British occupation and kingdom of Syria
When under Ottoman rule, stamps of Turkey are used in Syria. Austria, Egypt, France and Russia have offices abroad in Alexandrette and Latakia, Russia also has an office in Aleppo. In these offices the general issues from these countries or the issues for the Levant are used. The offices are closed in 1914. Following the occupation by British forces in 1918 and 1919, the issues from the Egyptian Expeditionary Force are used. These issues – inscribed ‘E.E.F.’ – are used in several territories occupied by the British, including Lebanon, Palestine, Syria and (Trans-)Jordan and are mostly cataloged with Palestine. The Arab Government and the kingdom of Syria issue stamps in 1920. These are overprints on Turkish stamps reading ‘Arab Government’ or ‘Syrian Arab Government’ in Arabic and are issued for use in Aleppo, Damascus, Homs and Hama. One set of definitives is issued for use in Damascus.
French occupation
As the French move into Syria from 1919, they first issue stamps as part of the OTEA. These are French and French Levant issues overprinted ‘T.E.O.'[2]‘Territoires Ennemis Occupés’ and a new face value. Some of these are used also in Cilicia at the time when it is occupied by the French. The ‘T.E.O.’ issues are, in 1920, succeeded by stamps issued by the French military administration, these being stamps of France and the kingdom of Syria overprinted ‘O.M.F. Syrie'[3]‘Occupation Militaire Française Syrie’ and a new face value. Local issues appear in 1920 for use in Aleppo due to a different currency used in that city. The issues show an additional control monogram on the previous O.M.F. issues. Yvert & Tellier also lists a local issue from 1921 with the ‘O.M.F.’ overprint now on Turkish Stamps for use in Ain Tab[4]The current Gaziantep. in Turkey. In Kilis – currently, also in Turkey – a local stamp is issued in 1921 when a large influx of Armenian refugees causes shortages of the regular issues. It is a hand stamped issue with sewing machine perforation.
French mandated territory
In 1923, the French civil administration issues stamps for the entire mandated territory of Syria and Greater Lebanon, French stamps overprinted ‘Syrie-Grand Liban’. In 1924, the postal administrations of Syria and Greater Lebanon are separated and, from then on, stamps are issued specifically for Syria. The first issues are still overprints on French stamps, the overprint now being ‘Syrie’, first only in French then in Arabic and French. The first definitives are issued in 1925. The Alawite State, as it is separated from Syria in 1924, issues its own stamps from 1925. In the Sandjak of Alexandrette the stamps of Syria have been used until 1938. Although resources used are not explicit on the subject one would suppose that the stamps of Syria have also been used in the State of Jabal al-Druze that was self governing until 1936.
Free French Forces in the Levant
When, in 1941, Free French Forces are deployed in Syria and Lebanon, stamps are issued for use by these forces in the field post offices. These are both overprints on Syrian stamps and stamps of specific design for the Free French Forces. The overprints and inscriptions on the issues for regular mail read ‘Forces Françaises Libres Levant’[5]‘Free French Forces Levant’ . Airmail issues are overprinted ”Lignes Aeriennes F.A.F.L.’[6]‘Airlines of the Free French Air Forces’ or inscribed ‘Lignes Aeriennes de la France Libre’[7]‘Airlines of Free France’ . These stamps are used until the French forces leave Syria in 1946.
Independent Syria
Syria proclaims independence in 1941 and the first issue of the independent republic of Syria, in 1941, commemorates the proclamation of independence. Since then, Syria has issued stamps as the republic of Syria until 1958. When Syria is part of the United Arab Republic, with Egypt, stamps are issued that are inscribed ‘United Arab Republic’, ‘UAR’ or ‘Republique Arabe Unie’, with or without the addition of ‘Syria’ or ‘Syrie’. From 1961, Syria has issued stamps as the Arab republic of Syria.
For an overview of the political and postal developments in the form of a diagram, please refer to the country diagram of Syria & Greater Lebanon.
Album pages
← Previous page: Sri LankaNext page: Tajikistan →